What is breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation, sometimes referred to as a “breast aug” or “boob job” by patients, involves using breast implants or fat transfer to increase the size of your breasts. This procedure can also restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy, achieve a more rounded breast shape or improve natural breast size asymmetry. Breast augmentation is also referred to as augmentation mammoplasty. When fat from another part of the patient’s body is used to create the improved breast volume, the procedure is referred to as fat transfer breast augmentation.What breast augmentation surgery can do
- Increase fullness and projection of your breasts
- Improve balance of breast and hip contours
- Enhance your self-image and self-confidence
What breast augmentation surgery can’t do
Breast augmentation does not correct severely drooping breasts. A breast lift may be required along with a breast augmentation for sagging breasts to look fuller and lifted. Breast lifting can often be done at the same time as your augmentation or may require a separate operation. Your plastic surgeon will assist you in making this decision.Who is a good candidate for breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation is a deeply personal procedure, and it’s important that you’re doing it for yourself and not for someone else, even if that person has offered to pay for it. Patient satisfaction is high, specifically when they want the procedure themselves.
You may be a candidate for breast augmentation if:
- You are physically healthy and you aren’t pregnant or breastfeeding
- You have realistic expectations
- Your breasts are fully developed
- You are bothered by the feeling that your breasts are too small
- You are dissatisfied with your breasts losing shape and volume after pregnancy, weight loss or with aging
- You are unhappy with the upper part of your breast appearing “empty”
- Your breasts are asymmetrical
- One or both breasts failed to develop normally or have an elongated shape
If you’re considering surgery, spend some time reviewing breast augmentation photos and learning about what to expect during recovery. Preparation ahead of time helps patients have reasonable expectations and a smoother recovery.
What should I expect during a consultation for breast augmentation?
During your breast augmentation consultation be prepared to discuss:
- Why you want breast augmentation surgery, your expectations and the desired outcome
- Medical conditions, drug allergies and previous medical treatments
- Current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco and drug use
- Family history of breast cancer and results of any mammograms or previous biopsies
Your plastic surgeon will also:
- Evaluate your general health status and any pre-existing health conditions or risk factors
- Examine and measure your breasts, including detailed measurements of their size and shape, skin quality and placement of your nipples and areolas
- Take photographs
- Discuss your options and recommend a course of treatment
- Discuss likely outcomes of breast augmentation and any risks or potential complications
The consultation is the time to ask your plastic surgeon questions. To help, we have prepared a checklist of questions to ask your breast augmentation surgeon that you can take with you to your consultation.
It’s important to understand all aspects of your breast augmentation surgery. It’s natural to be nervous about it, whether it’s excitement for your anticipated new look or a bit of preoperative stress. Don’t be shy about discussing these feelings with your plastic surgeon.
What questions should I ask my plastic surgeon about arm lift surgery?
Use this checklist as a guide during your breast augmentation consultation:
- Are you certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery?
- Were you trained specifically in the field of plastic surgery?
- How many years of plastic surgery training have you had?
- Do you have hospital privileges to perform this procedure? If so, at which hospitals?
- Is the office-based surgical facility accredited by a nationally- or state-recognized accrediting agency, or is it state-licensed or Medicare-certified?
- Am I a good candidate for breast enhancement or breast enlargement?
- What will be expected of me to get the best results?
- Where and how will you perform my breast augmentation surgery?
- What shape, size, surface texturing, incision site and placement site are recommended for me?
- How long of a recovery period can I expect, and what kind of help will I need during my recovery?
- What are the risks and complications associated with my procedure?
- How are complications handled?
- How many additional implant-related operations can I expect over my lifetime?
- How will my ability to breastfeed be affected?
- How can I expect my implanted breasts to look over time? After pregnancy? After breastfeeding?
- What are my options if I am dissatisfied with the cosmetic outcome of my implanted breasts?
- How will my breasts look if I choose to have the implants removed in the future without replacement?
- Do you have breast augmentation before-and-after photos I can look at for this procedure and what results are reasonable for me?
What types of breast implants are available?
Saline breast implants
Saline breast implants are filled with sterile salt water. Should the implant shell leak, a saline implant will collapse and the saline will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body.
Saline breast implants provide a uniform shape, firmness and feel, and are FDA-approved for augmentation in women age 18 or older.
Structured saline breast implants
Structured implants are filled with sterile salt water, and contain an inner structure which aims to make the implant feel more natural.
Silicone breast implants
Silicone breast implants are filled with silicone gel. The gel feels a bit more like natural breast tissue. If the implant leaks, the gel may remain within the implant shell, or may escape into the breast implant pocket. A leaking implant filled with silicone gel will not collapse.
If you choose silicone implants, you may need to visit your plastic surgeon regularly to make sure the implants are functioning properly. An ultrasound or MRI screening can assess the condition of breast implants.
Silicone breast implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women age 22 or older.
Gummy bear breast implants
Form-stable implants are sometimes referred to as gummy bear breast implants because they maintain their shape even when the implant shell is broken.
The consistency of the silicone gel inside the implant is thicker than traditional silicone gel implants. These implants are also firmer than traditional implants.
Shaped gummy bear breast implants have more projection at the bottom and are tapered towards the top. If a shaped implant rotates, it may lead to an unusual appearance of the breast that requires a separate procedure to correct.
Placement of gummy bear implants requires a slightly longer incision in the skin.
Round breast implants
Round breast implants have a tendency to make breasts appear fuller than form-stable implants. Higher profile options can achieve even more projection.
Because round implants are the same shape all over, there is less concern about them rotating out of place.
Smooth breast implants
Smooth breast implants are the softest feeling. They can move with the breast implant pocket, which may give more natural movement.
Smooth implants may have some palpable or visible rippling under the skin.
Textured breast implants
Textured breast implants develop scar tissue to stick to the implant, making them less likely to move around inside of the breast and become repositioned.
Texturing offers some advantage in diminishing the risk of a tight scar capsule.
*It’s important to note that breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) occurs most frequently in patients who have breast implants with textured surfaces. For more information on BIA-ALCL, visit our BIA-ALCL Summary page. Discuss all benefits and risks related to your breast implant procedure with your board-certified plastic surgeon. Understanding all potential risk factors will help with better decision-making that is best for you and your health.
Implant manufacturers occasionally introduce new styles and types of breast implants, so there may be additional options available.
Whether you choose saline or silicone implants, it is important for you to monitor your breast implants and follow-up with your plastic surgeon for appropriate checkups.
What are the risks of breast augmentation?
The decision to have plastic surgery is extremely personal and you will have to weigh the potential benefits in achieving your goals with the risks and potential complications of breast augmentation. Only you can make that decision for yourself.
You will be asked to sign consent forms to ensure that you fully understand the procedure and any risks and potential complications.
Possible breast augmentation surgery risks include:
- Anesthesia risks
- Bleeding
- Hematoma
- Infection
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation
- Poor scarring
- Wrong or faulty position of the implant
- Implant leakage or rupture
- The formation of tight scar tissue around the implant (capsular contracture)
- Fluid accumulation (seroma)
- Wrinkling of the skin over the implant
- Persistent pain
- Possibility of revision surgery
These risks and others will be fully discussed prior to your consent. It is important that you address all your questions directly with your plastic surgeon.
Breast implant safety
Careful reviews of scientific research by independent groups such as the Institute of Medicine have found no link between breast implants and autoimmune or other systemic diseases.
Other important considerations:
- Breast implants are not guaranteed to last a lifetime and future surgery may be required to replace one or both implants
- Pregnancy, weight loss and menopause may influence the appearance of augmented breasts over the course of your lifetime
- Breast augmentation requires regular examinations of your breasts’ health and to evaluate the condition of your breast implants
How should I prepare for breast augmentation?
In preparing for breast augmentation, you may be asked to:
- Get a blood test
- Take certain medications or adjust your current medications
- Stop smoking
- Avoid taking aspirin and certain anti-inflammatory drugs as they can increase bleeding
- Stop taking recreational drugs, such as cocaine
Breast augmentation surgery should be performed in an accredited outpatient or ambulatory surgical center or a hospital. This is for your safety. If your surgeon has a may informal setting, he or she may not be a board-certified plastic surgeon.
If your breast augmentation is performed on an outpatient basis, arrange for someone to drive you to and from surgery and to stay with you for at least the first night following surgery.
What are the steps of a breast augmentation procedure?
A breast augmentation procedure includes the following steps:
Step 1 – Anesthesia
Medications are administered for your comfort during the surgical procedure. The choices include intravenous sedation and general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best choice for you.
Step 2 – The incision
Incisions are made in inconspicuous areas to minimize visible scarring. You and your plastic surgeon will discuss which incision options are appropriate for your desired outcome. Incision options include: along the areolar edge (peri-areolar incision), the fold under the breast (inframammary fold) and in the armpit (axillary incision). A belly-button approach is associated with a higher complication rate.
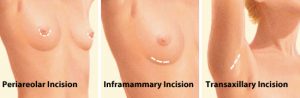
Incisions vary based on the type of breast implant, degree of enlargement desired, your particular anatomy and patient-surgeon preference.
Step 3 – Inserting and placing the breast implant
After the incision is made, a breast implant is inserted into a pocket either:
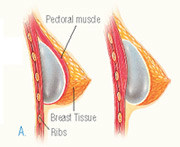
A. Under the pectoral muscle (a submuscular placement)
B. Directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle (a submammary/ subglandular placement)
The method for inserting and positioning breast implants depends on the type of implant, degree of enlargement desired, your body type and your surgeon’s recommendations.
Step 4 – Closing the incisions
Incisions are closed with layered sutures in the breast tissue and with sutures, skin adhesive or surgical tape to close the skin.

Over time the incision lines will fade. The quality of scar depends on many things, including your genetics, exposure of your body to nicotine and infection.
Step 5 – See the results
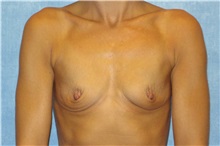
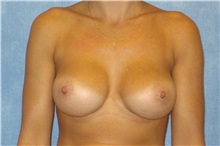
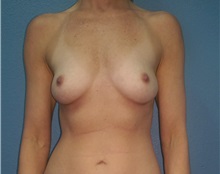
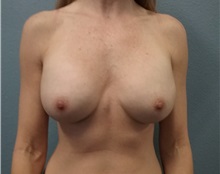
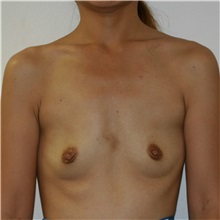
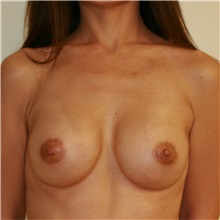
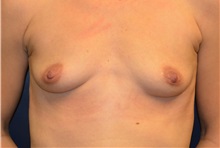
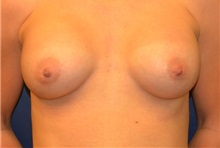
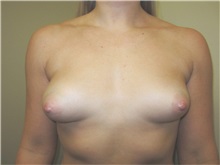
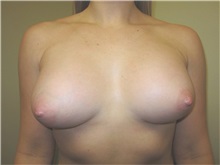
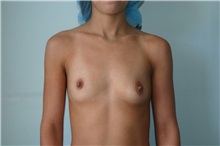
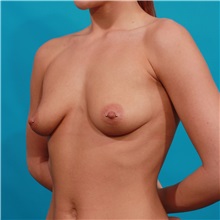
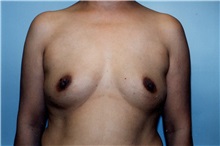
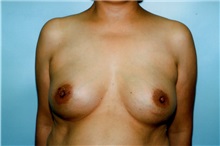
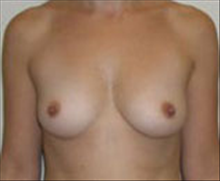
The results of breast augmentation are immediately visible. Get more information about breast augmentation results.
What should I expect during my breast augmentation recovery?
During your breast augmentation recovery, your breasts will be wrapped in gauze dressings and an elastic bandage or support bra will minimize swelling and support the breasts as they heal.
Immediately after surgery, you will be taken into a recovery area for close monitoring. You may be permitted to go home when you are stable for discharge, typically after an hour or so.
Before leaving, you will be given specific postoperative instructions for your breast implant recovery and a follow-up appointment with your plastic surgeon. You may also receive medications or a prescription, but many plastic surgeons prescribe postoperative medications in advance. Your prescribed medications may include pain pills and an antibiotic to prevent infection.
Wear your support garment (a bra or elastic band, called a bandeau) around the clock as instructed by your plastic surgeon. Some surgeons may ask patients cleanse the incision sites and apply ointment, while others will ask their patients to keep tape or a bandage on. Instructions vary, so it’s important to follow all your plastic surgeon’s directions carefully.
Because it is possible to bleed into the pockets around the breast implants for the first several days, take it easy until you have permission to increase your activity level. Acute pain typically subsides after one to five days, but you may experience soreness and swelling for a few weeks. Resume exercise and normal activity according to your plastic surgeon’s directions.
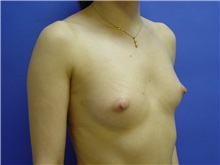
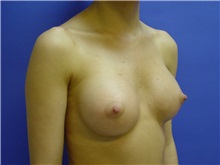
What results should I expect after breast augmentation surgery?
While a breast augmentation yields larger breasts right away, the final results may take a few weeks as the swelling subsides and the skin stretches. Some patients may need to wear a bandeau to help shape their breasts, especially if they have underlying asymmetry or very small breasts to start with. Incision lines may take several months, even a couple of years, to fade.
To achieve optimal breast augmentation results, follow your surgeon’s post-operative instructions and return for follow-up visits.
Breast implant replacement
Breast implants are not considered to be lifetime devices, and they may need to be replaced. You can see your plastic surgeon for an annual examination to evaluate your breast health and implant integrity.
Over time, your breasts will change due to aging, weight fluctuations, hormonal factors and gravity. As the appearance of their breasts changes with time, some patients have a breast lift or an implant exchange to restore a more youthful contour.
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
What words should I know about breast augmentation?
Areola
Pigmented skin surrounding the nipple.
Augmentation mammaplasty
Breast enlargement or breast enhancement by surgery.
Breast augmentation
Also known as augmentation mammaplasty; breast enlargement or breast enhancement by surgery.
Breast implants
Medical devices placed in your body to enhance an existing breast size or to reconstruct your breast. Breast implants fall into two categories: saline breast implants and silicone breast implants.
Capsular contracture
A complication of breast implant surgery which occurs when scar tissue that normally forms around the implant tightens and squeezes the implant and becomes firm.
General anesthesia
Drugs and/or gasses used during an operation to relieve pain and alter consciousness.
Hematoma
Blood pooling deep to the skin.
Inframammary incision
An incision made in the fold under the breast.
Intravenous sedation
Sedatives administered by injection into a vein to help you relax.
Local anesthesia
A drug injected directly to the site of an incision during an operation to relieve pain.
Mammogram
An x-ray image of the breast.
Mastectomy
The removal of breast tissue, typically to rid the body of cancer.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging; a painless test to view tissue similar to an x-ray.
Periareolar incision
An incision made at the edge of the areola.
Saline implants
Breast implants filled with sterile salt water.
Silicone implants
Breast implants filled with an elastic gel.
Submammary or subglandular or subfascial placement
Breast implants placed directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle.
Submuscular or subpectoral placement
Breast implants placed under the pectoral muscle, which is located between the breast tissue and chest wall.
Sutures
Stitches used to hold skin and tissue together.
Transaxillary incision
An incision made in the underarm area.
Ultrasound
A diagnostic procedure that projects high-frequency sound waves into the body and records the echoes as pictures.
How do I choose a plastic surgeon for breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation surgery involves many choices. The first and most important is selecting a board-certified plastic surgeon you can trust who is a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
ASPS member surgeons meet rigorous standards:
- Board certification by the American Board of Plastic Surgery® (ABPS) or in Canada by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada®
- Complete at least six years of surgical training following medical school with a minimum of three years of plastic surgery residency training
- Pass comprehensive oral and written exams
- Graduate from an accredited medical school
- Complete continuing medical education, including patient safety, each year
- Perform surgery in accredited, state-licensed, or Medicare-certified surgical facilities
Do not be confused by other official-sounding boards and certifications.
The ABPS is recognized by the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS), which has approved medical specialty boards since 1934. There is no ABMS recognized certifying board with “cosmetic surgery” in its name.
By choosing a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, you can be assured that you are choosing a qualified, highly-trained plastic surgeon who is board-certified by the ABPS or the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
